The Complete UK Student Guide for 2025-2026
Writing a strong and compelling research proposal is the foundation of your academic success—especially if you’re applying for a Master’s, MPhil, or PhD programme in the UK. Top universities such as Oxford, Cambridge, UCL, King’s College London, Manchester, Glasgow, Leeds, and many others expect a proposal that demonstrates not just your idea, but your clarity of thought, depth of understanding, and ability to conduct independent research.
A well-written research proposal does far more than outline a topic.
It shows the admissions committee:
✨ Why your research matters
✨ What gap it will fill in existing knowledge
✨ How feasible your study is in terms of scope, time, and resources
✨ Why you are the right person to conduct this research
In short, a strong proposal convinces the university that your research is valuable, original, and academically significant.
At ProjectsDeal – UK’s Most Trusted Academic Writing Service Since 2001, we have supported thousands of students in crafting impactful, supervisor-approved research proposals. Our experts understand exactly what UK universities expect, how to present your ideas convincingly, and how to structure a proposal that stands out in a competitive academic environment.
Whether you’re struggling with choosing a topic, defining your research problem, building a solid methodology, or structuring your chapters, this guide will walk you through every key step with clarity and confidence.
From selecting a meaningful research area to designing your timeline, budget, and references—this comprehensive guide ensures you have everything you need to create a proposal that secures approval the first time.
⭐ Quick Overview: How to Write a Research Proposal
To write a research proposal, you should:
- Define your topic, research questions, and objectives
- Structure your proposal with: Introduction & Background, Literature Review, Methodology
- Explain data collection and analysis methods
- Include a timeline, budget (if needed), and references
- Show importance, feasibility, and originality
Key Tips:
- Follow university guidelines
- Be persuasive and clear
- Seek feedback from supervisors or mentors
What is a Research Proposal? (Complete UK Student Explanation)
A research proposal is much more than just a document—
it is the blueprint of your academic vision, the roadmap of your study, and the first impression you make on the admissions committee or potential supervisor.
Think of it as your opportunity to convince the university that:
- Your topic is interesting
- Your study is important
- Your plan is achievable
- You are prepared and capable of conducting the research
In simple terms, a research proposal is a formal document that clearly outlines:
📌 What you want to research
The core topic, problem, or issue you want to explore.
📌 Why the research matters
Its significance, practical relevance, and contribution to the academic world or real-world problems.
📌 How you will conduct the research
The methods, tools, data sources, and approach you will use to answer your research questions.
📌 What outcomes or contributions you expect
What your study hopes to achieve and how it will benefit academia, industry, or future researchers.
Why UK Universities Require a Research Proposal
In the UK, especially in top-tier universities, a research proposal is a critical part of the application process. It allows the admissions panel to:
✔ Evaluate your understanding of the topic
They want to see that you’ve done your homework and understand the key issues in your research area.
✔ Assess whether the study is realistic and academically valuable
Your topic must be achievable within your programme’s timeframe and contribute meaningfully to existing research.
✔ Determine whether they can assign a suitable supervisor
Universities match you with a supervisor who specialises in your field—your proposal helps them identify the right expert.
✔ Decide on your admission into MSc/MPhil/PhD programmes
A strong research proposal significantly increases your chances of acceptance, scholarship consideration, and supervisor approval.
Ideal Length of a UK Research Proposal
| Academic Level | Ideal Word Count | What UK Universities Expect at This Level |
|---|---|---|
| Master’s (MSc, MA, MBA, MRes) | 1,500 – 2,500 words | A concise proposal showing understanding of the topic, clear objectives, a basic literature review, and a feasible methodology suitable for a short-term study. |
| MPhil | 2,500 – 4,000 words | A more detailed proposal demonstrating deeper theoretical background, a stronger research gap, and a more refined methodology. Shows readiness for independent research training. |
| PhD | 3,000 – 5,000 words | A comprehensive proposal showing originality, a significant research gap, detailed methods, feasibility of a multi-year project, expected contribution to knowledge, and strong academic justification. |
Important Note
Always check your university or department’s specific guidelines, as word limits and structure can vary based on discipline, programme type, and supervisor preferences.
🎯 Key UK Universities & Their Research Proposal Guidance
You can create a grid layout with logos on the left and guidance text on the right for each university. Example format:
| University | Research Proposal Guidance / Key Requirements |
|---|---|
 | University of Oxford – Requires a research proposal for many postgraduate courses. Emphasises strict adherence to word counts, originality, and alignment with course requirements. |
 | University of Cambridge – Proposals must respect department-specific word limits and formatting. Ensure clarity, focus, and relevance to the field of study. |
 | University of Manchester – Evaluated on intellectual purpose, originality, clear topic definition, and knowledge of the research context. Typical length around 1,000–1,500 words. |
| | University of Leeds – Includes working title, context and literature overview, research aims, methodology, realistic plan/timescale, expected outcomes, and references. |
 | University of Edinburgh – Applicants must describe the importance, scope, and plan for conducting research. Proposals should be clear, realistic, structured, may include headings or diagrams. |
 | University of Birmingham – Expected length varies (1,000–1,500 words for most programmes, 2,500 for some law programmes). Include subject, aims/objectives, and methodological approach. |
 | King’s College London – Proposals must show research feasibility, clarity, and originality. Includes clear aims, objectives, methodology, and timeline. |
| | University College London (UCL) – Detailed methodology, strong theoretical grounding, and research feasibility are emphasised. Structure and length vary by programme. |
| | University of Glasgow – Well-structured proposal demonstrating originality, clear aims, methodology, and realistic timeline. Often includes expected outcomes and references. |
 | University of Warwick – Define research aims, objectives, methodology, and significance. Focus on clarity, logical flow, and feasibility. |
Full Structure of a UK Research Proposal (Step-by-Step)
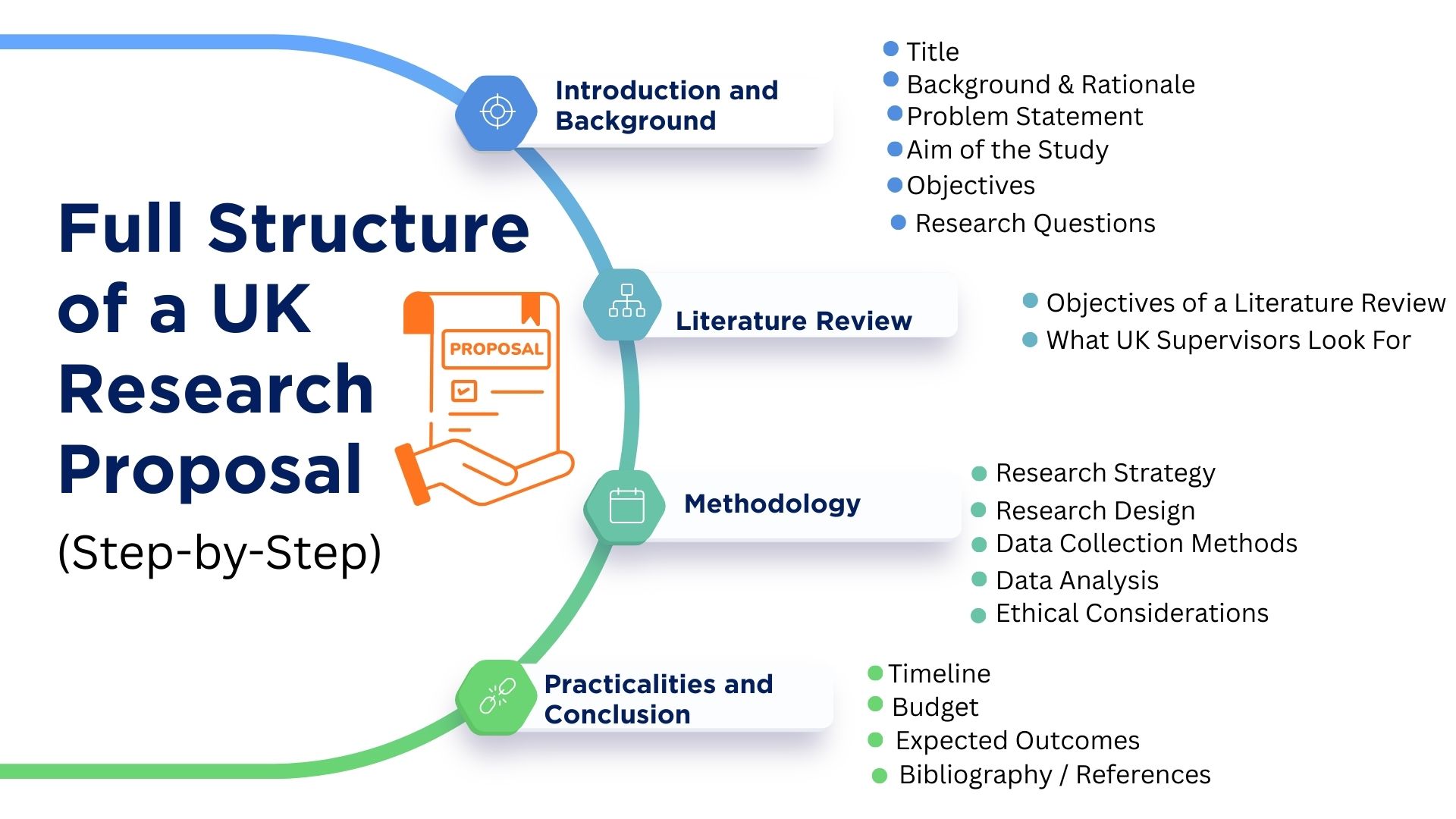
1. Introduction and Background (The Foundation of Your Proposal)

The Introduction and Background section sets the tone for your entire research proposal. It must be clear, engaging, and academically strong—showing your university exactly what you want to research and why it truly matters.
Below is an enhanced, polished version with examples added for every part.
a. Title
Your title should be:
✔ Clear
✔ Concise
✔ Aligned with your research focus
✔ Reflective of your approach or context
Think of it as the “headline” of your research.
Example Titles
- “AI Adoption and Customer Experience: A Study of UK Retail Banking”
- “The Impact of Social Media Marketing on SME Growth in London”
- “Nursing Burnout and Patient Safety: A Mixed-Methods Study in NHS Hospitals”
- “Sustainability Practices and Consumer Behaviour in the UK Fashion Industry”
b. Background & Rationale
This is where you set the stage.
Explain:
- What your topic is about
- Where the problem exists
- Why the study is timely and important
- What gaps or challenges currently exist
- Why this topic matters in the real world
Example (Short & Effective)
The rapid adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) in the UK banking sector is transforming customer interactions. While AI technologies promise faster service and improved efficiency, concerns remain about personalisation, trust, and customer satisfaction. Understanding how AI affects the overall customer experience is essential for banks aiming to maintain competitiveness and customer loyalty.
c. Problem Statement
The problem statement explains the specific issue your study will address.
It should be clear, focused, and researchable.
Example
Although UK retail banks have widely implemented AI tools such as chatbots and automated support systems, little is known about how these technologies influence customer satisfaction and trust. This lack of clarity creates challenges for banks as they invest in AI without fully understanding its impact.
d. Aim of the Study
Your aim is the overall purpose of your research.
It should be a single, strong sentence.
Example
The aim of this study is to evaluate the impact of AI-based customer service tools on customer experience in UK retail banking.
e. Objectives
Objectives break your aim into manageable steps.
They should be specific, measurable, and achievable.
Example Objectives
- To examine customer perceptions of AI-driven services in UK retail banks.
- To analyse the factors that influence trust and satisfaction in AI banking interactions.
- To compare AI-based services with traditional human-assisted services.
- To identify challenges and opportunities for improving AI-driven customer experience.
f. Research Questions
Research questions guide your entire study.
They must align directly with your objectives.
Example Research Questions
- How do customers perceive the use of AI technologies in UK retail banking?
- What factors influence customer trust when interacting with AI-driven services?
- How does customer satisfaction with AI-based service compare to human-assisted service?
- What improvements can UK banks make to enhance AI-based customer experience?
💡 Pro Tip from ProjectsDeal.co.uk:
Your aim → objectives → research questions must flow logically. If an objective does not connect to a research question, remove or reword it. A well-aligned proposal makes it easier for supervisors and universities to understand your research plan and see its feasibility.
How ProjectsDeal Helps
ProjectsDeal guides UK students in creating clear titles, strong background, and well-aligned aims, objectives, and research questions. Our experts ensure your proposal is polished, logical, and submission-ready, helping you impress supervisors from the very first section.
2. Literature Review (Demonstrating Academic Depth & Originality)

The literature review is a critical part of your research proposal. It shows that you understand the current state of knowledge in your field and can position your study as an original and valuable contribution.
A strong literature review does more than summarise existing research—it analyses, evaluates, and connects findings to your own research questions.
Key Objectives of a Literature Review
Your literature review should:
- Demonstrate familiarity with existing research
Show that you know the key studies, authors, and trends in your field. - Analyse key theories, models, and debates
Don’t just describe studies—critically evaluate methodologies, strengths, limitations, and conclusions. - Identify the current gap in the literature
Highlight what is missing or understudied. This is your opportunity to justify the need for your research. - Show how your research will provide an original contribution
Clearly explain what new insights your study will add. - Prove your study is academically justified and relevant
Ensure your proposal aligns with theoretical, practical, or policy needs.
What UK Supervisors Look For
When reviewing literature, UK supervisors pay attention to:
- Theoretical grounding – Are your sources well-theorised and credible?
- Logical flow – Is the literature review structured in a coherent, organised way?
- Recent sources – Are the majority of references from the last 5 years, showing up-to-date research?
Example of a Literature Review (Banking AI Study)
Topic: AI Adoption and Customer Experience in UK Retail Banking
Previous studies have explored the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in global banking, focusing primarily on operational efficiency and cost reduction (Smith, 2020; Lee & Kim, 2021). However, only a few studies have investigated the customer experience dimension, particularly in the UK context. Johnson (2019) found that AI chatbots improved response times but reduced perceived personalisation. Meanwhile, Patel (2022) highlighted trust issues arising from automated customer interactions. Despite these insights, there is a lack of research exploring the combined effect of AI adoption on both customer satisfaction and trust in UK retail banks. This study aims to fill this gap by analysing customer perceptions and comparing AI-driven services with traditional human-assisted services, thereby providing an original contribution to both academic knowledge and industry practice.
💡 Pro Tip from ProjectsDeal.co.uk:
Always link the literature to your research questions. Each paragraph should help justify why your study is needed and how it will advance knowledge. Use recent peer-reviewed sources (last 5 years) to show your research is current, credible, and relevant.
How ProjectsDeal Helps
ProjectsDeal helps UK students create focused, well-structured literature reviews that identify gaps, analyse key studies, and clearly link findings to your research objectives—making your proposal persuasive and academically strong.
3. Methodology (The Most Critical Section for UK Universities)

The methodology section is the heart of your research proposal. It shows how you plan to answer your research questions, and UK universities scrutinise it closely to assess feasibility, academic rigour, and ethical standards.
A strong methodology demonstrates that your study is well-planned, achievable, and credible.
a. Research Strategy
Your research strategy outlines the overall approach to your study. Choose one:
- Qualitative: Focuses on understanding behaviours, perceptions, or experiences. Common methods include interviews, focus groups, or thematic analysis.
- Quantitative: Focuses on measurable data and statistical analysis. Common methods include surveys, experiments, or regression analysis.
- Mixed Methods: Combines qualitative and quantitative approaches to provide a fuller understanding of your research problem.
Example:
For a study on AI adoption in UK banking, a mixed-methods approach can be used: qualitative interviews with customers to understand perceptions, and quantitative surveys to measure satisfaction levels across a larger population.
b. Research Design
Your research design explains how the study will be structured. Common designs include:
- Exploratory: To explore new or under-researched areas.
- Descriptive: To describe patterns, behaviours, or phenomena.
- Explanatory: To investigate cause-and-effect relationships.
- Experimental: To test hypotheses in a controlled environment.
Example:
An explanatory research design could be used to examine how AI adoption in UK retail banks influences customer satisfaction and trust.
c. Data Collection Methods
This section specifies what data you will collect, and how.
Include:
- Primary or Secondary Data: Will you collect original data or use existing sources?
- Tools & Techniques: Surveys, interviews, questionnaires, experiments, observations.
- Sampling: Size, selection criteria, and sampling technique (e.g., random, purposive, stratified).
- Target Population: Who will provide the data (e.g., UK retail bank customers, NHS nurses, university students).
Example:
Primary data will be collected through online surveys distributed to 200 UK retail bank customers and in-depth interviews with 10 selected participants to explore trust and satisfaction in AI banking interactions.
d. Data Analysis
Explain how you will process and interpret your data. Use techniques appropriate to your research strategy.
Qualitative Techniques:
- Thematic analysis
- Content analysis
Quantitative Techniques:
- Regression analysis
- ANOVA
- Descriptive and inferential statistics (SPSS, Excel)
Example:
Survey data will be analysed using SPSS to calculate descriptive statistics and regression analysis, while interview transcripts will undergo thematic analysis to identify key patterns in customer perceptions.
e. Ethical Considerations
UK universities place high importance on ethics. You must demonstrate that your research respects participants and data protection rules.
Key points to include:
- Informed Consent: Participants must agree to take part after understanding the study.
- Confidentiality: Keep participants’ identities and responses private.
- Data Protection (GDPR): Safely store, manage, and use data.
- Ethical Approval: Obtain approval from your university’s ethics committee if required.
Example:
All participants will provide written consent before the survey. Data will be anonymised and stored securely, complying with GDPR. Ethical approval will be obtained from the university’s Ethics Committee prior to data collection.
💡 Pro Tip from ProjectsDeal.co.uk:
Your methodology should be specific, detailed, and realistic. Clearly justify every choice—from research strategy to data analysis—to show supervisors that your study is feasible, credible, and academically sound. Avoid vague statements like “I will collect data from participants” without specifying how, who, and why.
How ProjectsDeal Helps
ProjectsDeal helps UK students create a clear, feasible, and university-ready methodology by guiding research strategy, design, data collection, analysis, and ethical compliance—making your proposal credible and supervisor-ready.
4. Practicalities and Conclusion (Planning for Success)

The practicalities section of your research proposal shows UK universities that your study is well-organised, feasible, and realistic. It also highlights that you’ve considered time, resources, and expected outcomes—which makes your proposal much stronger.
a. Timeline
A clear, realistic timeline demonstrates that you can complete your research within your programme duration. Break it down into phases:
- Literature Review: Identify key studies and theories
- Methodology Development: Plan data collection methods and tools
- Data Collection: Gather primary or secondary data
- Data Analysis: Process and interpret findings
- Writing: Draft chapters and compile results
- Revision & Submission: Proofread, edit, and finalise
Many students present their timeline visually using a Gantt chart to make it easier for supervisors to see the schedule at a glance.
Example Timeline (6-Month MSc Project)
| Phase | Month |
|---|---|
| Literature Review | 1–2 |
| Methodology Development | 2–3 |
| Data Collection | 3–4 |
| Data Analysis | 4–5 |
| Writing Draft | 5–6 |
| Revision & Submission | 6 |
b. Budget (If Required)
If your research requires funding, include a realistic budget showing the resources you need.
Items may include:
- Tools/Software: SPSS, NVivo, Excel, survey platforms
- Travel Expenses: Field visits, interviews, or observations
- Survey Tools: Online survey subscriptions or printing costs
- Equipment: Recorders, lab materials, or specialised instruments
Example Budget (UK Retail Banking Study)
| Item | Cost (£) |
|---|---|
| Online survey subscription | 50 |
| Travel for interviews | 100 |
| Data analysis software (SPSS) | 120 |
| Printing & materials | 30 |
| Total | £300 |
c. Expected Outcomes
Clearly explain what you expect to discover and how it will contribute to your field. UK universities value research that is original, relevant, and impactful.
Example Expected Outcomes (AI Banking Study)
- Identification of key factors affecting customer trust and satisfaction with AI services
- Recommendations for banks to improve AI implementation and customer engagement
- Academic contribution: filling the research gap on AI and customer experience in UK retail banking
- Practical relevance: helping banks make data-driven decisions and improve service quality
d. Bibliography / References
Your references demonstrate academic rigour and show that your research is grounded in credible literature.
- Use an appropriate referencing style: Harvard, APA, MLA
- Include peer-reviewed, academic, and recent sources (preferably last 5 years)
- Ensure every citation in the text matches your reference list
Example References
- Johnson, R. (2019). Customer Experience in AI Banking. London: Routledge.
- Patel, S. (2022). Trust and Automation in UK Retail Banks. Journal of Banking Studies, 34(2), 120–135.
- Smith, J. (2020). AI Technologies in Modern Banking. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
💡 Pro Tip from ProjectsDeal.co.uk:
A clear timeline, budget, expected outcomes, and references make your proposal look professional and feasible. Always align your practical plans with your research objectives—this shows supervisors that you’ve thought through every detail and can successfully complete the project on time and within resources.
How ProjectsDeal Helps
ProjectsDeal helps UK students create professional, submission-ready proposals with a clear timeline, accurate budgets, strong outcomes, and properly formatted references—making your proposal convincing and ready for approval.
⚠️ Common Research Proposal Challenges & How ProjectsDeal Helps
Many UK students struggle when writing research proposals. The main challenges include:
| Challenge | Why It Happens | How ProjectsDeal Solves It |
|---|---|---|
| Choosing a Research Topic | Students often pick topics that are too broad, too narrow, or lack originality. | Our expert writers help you select a feasible, relevant, and original topic tailored to your programme. |
| Formulating Research Questions & Objectives | Difficulty in aligning objectives with the overall aim or creating focused questions. | We craft clear, aligned, and academically strong research questions and objectives. |
| Conducting a Literature Review | Students struggle to find credible sources, analyse literature, and identify research gaps. | ProjectsDeal provides comprehensive literature reviews with critical analysis and identification of gaps. |
| Designing Methodology | Confusion over qualitative vs. quantitative methods, data collection, and analysis techniques. | We prepare a detailed, UK-university-compliant methodology, including research strategy, data collection, and analysis. |
| Structuring the Proposal | Poor flow, missing sections, or inconsistent formatting. | Our experts ensure proper structure, logical flow, and adherence to university guidelines. |
| Time Management | Tight deadlines make it hard to complete high-quality proposals. | ProjectsDeal offers fast delivery and can meet urgent deadlines without compromising quality. |
| Ensuring Academic Standards | Plagiarism, referencing errors, and weak academic tone. | All proposals are 100% plagiarism-free, properly referenced, and written in professional academic tone. |
Important Tips for Writing a Research Proposal (UK-Focused)
| Tip | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 1. Always Check Institutional Guidelines | Follow your university’s requirements for formatting, word count, structure, and referencing style. |
| 2. Make Your Proposal Persuasive | Convince readers that your research is important, feasible, and academically valuable. |
| 3. Show Ability to Conduct Independent Research | Demonstrate that you can plan, execute, and analyse research on your own. |
| 4. Use an Academic Tone & Avoid Vague Language | Be clear, precise, and professional; avoid casual or ambiguous phrases. |
| 5. Demonstrate Originality | Highlight how your study fills a gap or provides new insights to the field. |
| 6. Ensure All Sections Connect Clearly & Logically | Make sure the aim, objectives, research questions, methodology, and expected outcomes flow seamlessly. |
| 7. Seek Feedback from a Supervisor or Mentor | Getting input helps identify inconsistencies, gaps, or unclear phrasing. |
| 8. Proofread for Structure, Clarity & Coherence | Correct grammar, spelling, and logical flow show professionalism and attention to detail. |
Common Mistakes UK Students Should Avoid
❌ Too broad or vague topic
❌ Weak or generic methodology
❌ No clear research gap
❌ Outdated references
❌ Poor alignment between aim, objectives, and research questions
❌ Lack of feasibility
❌ Copying online templates without customisation
❓ FAQ: Research Proposal Writing (UK Students)
1. What is the format of a research proposal?
A proposal includes Title, Introduction, Literature Review, Methodology, Timeline, Budget, and References. ProjectsDeal ensures your proposal follows the correct format.
2. How do you start writing a research proposal?
Begin with a focused topic, aims, objectives, and research questions. ProjectsDeal helps you start strong with expert guidance.
3. Can ChatGPT write a research proposal?
ChatGPT can assist with ideas, but ProjectsDeal provides complete, original, and high-quality proposals.
4. How to write a PhD research proposal in the UK?
Focus on originality, feasibility, and methodology. ProjectsDeal helps craft well-structured, university-ready proposals.
5. What is the basic structure of a research proposal?
Title, Introduction, Literature Review, Research Questions/Objectives, Methodology, Timeline/Budget, Expected Outcomes, References. ProjectsDeal ensures perfect structure and flow.
6. How long should a research proposal be?
- Master’s: 1,500–2,500 words
- MPhil: 2,500–4,000 words
- PhD: 3,000–5,000 words
ProjectsDeal helps you stay within limits while keeping content strong.
7. Is it hard to write a research proposal?
It can be challenging, but ProjectsDeal makes it simple and stress-free with expert support.
8. What are the five steps in writing your proposal?
- Topic selection
- Define aims/objectives
- Literature review
- Methodology planning
- Timeline & references
ProjectsDeal guides you through all steps smoothly.
9. What are the 7 steps of the research process?
Identify problem → Review literature → Formulate questions → Design methodology → Collect data → Analyse → Report results. ProjectsDeal supports every step efficiently.
10. Which AI is best for a research proposal?
ChatGPT is helpful for ideas, but ProjectsDeal combines AI support with expert human guidance for full proposals.
11. What are the 7 steps of writing a research paper?
Topic → Literature → Thesis → Methodology → Data collection → Analysis → Write & reference. ProjectsDeal helps students complete all steps professionally.
12. What are the four types of research proposals?
Solicited, Unsolicited, Pre-Proposal, Continuation. ProjectsDeal can assist with any type, tailored to your needs.
Get Expert Help with Your Research Proposal – Trusted by UK Students
When it comes to writing research proposals that get approved and impress supervisors, UK students trust ProjectsDeal for expert support. Here’s why you should too:
🚀 Most Trusted Dissertation & Proposal Writing Service Since 2001
🎓 Specialist Writers for MBA, MSc, Nursing, Psychology, Law, Engineering
📚 100% Plagiarism-Free and original research proposals
🕒 Fast Delivery & urgent deadlines accepted
💬 24/7 WhatsApp Support
🔐 100% Confidential
Don’t leave your research proposal to chance—get professional, expert help today and submit with confidence!
📱 WhatsApp: +44-7447-882377
🌐 Website: www.projectsdeal.co.uk
🏆 Recognised for Excellence: ProjectsDeal.co.uk was voted one of the best academic writing services in the UK. Read more here.
